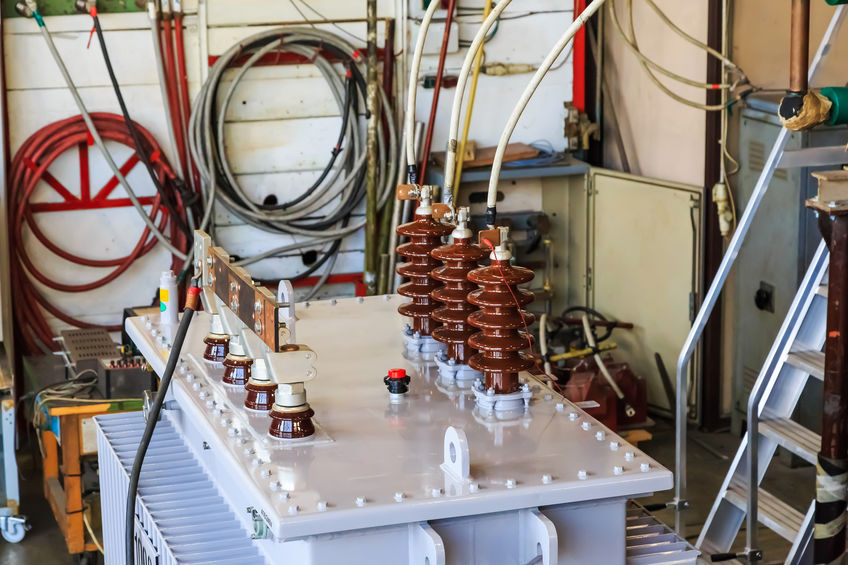
An HV power distribution system simply means a high voltage distribution system while an LV is a low voltage or tension power distribution system. LV power supply can be around 230 Volts for a single-phase connection and 400 Volts for a three-phase connection.
On the other hand, the HV distribution system can even reach 11Kilo-Volts, meaning it is highly used by bulk power purchasers like industries, hostels, big offices, and colleges. This article gives more insights regarding HV and LV power distribution systems.
Learn More About Our Company:
ABOUT US | OUR PRODUCTS | CONTACT US
Differences between HV and LV Power Rates
Rating
LV cables normally carry voltage below 1100V while high voltage power lines carry above 3300V.
Conductors
Aluminum and copper are the most used conductors for LV and HV cables.
Insulation
Because overhead power lines are not covered by insulation, there are many safety considerations when working and playing nearby. Both LV and HV cables have insulation layers to protect the cables from external elements. LV cables use materials like PVC while HV cables normally use cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE).
Armoring
Armoring is the protective covering for a cable and is present in both LV and HV cables. However, some LV cables can be unarmored.
Number of Cores
LV cables comprise of 1 or 2 cores but can extend to 61 cores while HV cables comprise of aluminum or stranded copper cores. They are usually 1 or 3 cores.
Application
LV cables are mostly used in industries like power stations, power distribution, and railways that require a maximum of 1100V. On the other hand, HV cables are normally used in power distribution or transmission with a range above 1100V.
You can read about What is the Difference Between a Busbar and a Feeder in this article.
HV and LV Power Rates
Power distribution companies offer electricity at different rates to different kinds of consumers. Every state has its own categories, which cater to the distinct needs of its residents and businesses. However, the most common categories include residential, industrial, and commercial. The rates are lowest for residential users and highest for industrial users. Let us have a look at these rates in detail:
Domestic Rates
Domestic LV is most applicable for residential areas, including those in rural and urban regions. On the other hand, domestic HV mostly entails a bulk supply for residents. At most times, the connected load usually differentiates the categories because commercial units can be located in the housing society and the rates can increase if the connected load is high.
Commercial & Industrial Rates
The structure of industrial and commercial rates is quite different compared to domestic. For these two, every state will have its own unique structure.
Although the cost of power generation and distribution is the same, the rates charged for consumers can be quite different. For instance, if the average cost of service is $0.10 per unit, a domestic user can pay $0.08 per unit while an industrial user can pay $0.15 per unit. In such a case, the domestic user can be said to be cross-subsidized by the industrial customer. Such cross-subsidies are put in place to make sure the common individual is not burdened by increasing electricity costs.
The Impact of Increasing HV Lines
Increasing HV lines can assist to reduce both voltage drops and line losses. Let us have a look at these two points in detail.
In this article, we review What is Cable Bus? Superior Cable Bus Explained.
Reduction in Voltage Drops
Voltage drops in LV cables can be high because lines are long and have small conductor sizes. HV power distribution systems usually have the voltage drop for the distribution of power to be less than 1% compared to that in low voltage systems. This makes sure there is a good voltage profile for the average consumer.
Reduction in Line Losses
In a low voltage power distribution system, the supply at a low voltage can lead to high line losses. However, the line loss in a high tension system for the distribution of a similar amount of power is less than 1% of the entire LV system. Therefore, with a high tension power distribution system, the overall energy losses are significantly reduced.
With all factors such as load factor and power factor remaining constant, percentage loss in a system having a high LV/HV ratio is usually higher than in a distribution system with a less LV/HV ratio.
A power distribution system is more than just a couple of wires transmitting electricity. It is comprised of cables, which carry both high tension and low tension. The cables are the most important element of the entire power distribution system because they help carry power from one point to another. Cables come in distinct sizes and voltage range. HV cables can carry above 3300V while LV cables normally support 600-1100V.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is A High Tension Line?
A high-tension electricity cable is one which is able to carry a very powerful current. A high-tension cable carries more than 1000 Volts between conductors and 600 Volts between conductors and ground. You need very high voltage for transmission on high-tension power lines.
What is the difference between HT and LT cable?
LT cables can be utilized in 1.1 kV range-related businesses including electricity distribution, power plants, trains, etc. While power transmission and distribution with a range greater than 1.1 kV uses HT cables.
Resources
- How Much Voltage Drop Can a Busbar Withstand?
- What is Relay and Busbar?
- What are the Basics of Electric Power Distribution System?
- What are Some Examples of a Bus in Electronics?