-
SuperiorBus Installation Guide for Cable Bus Electric Power Distribution Systems
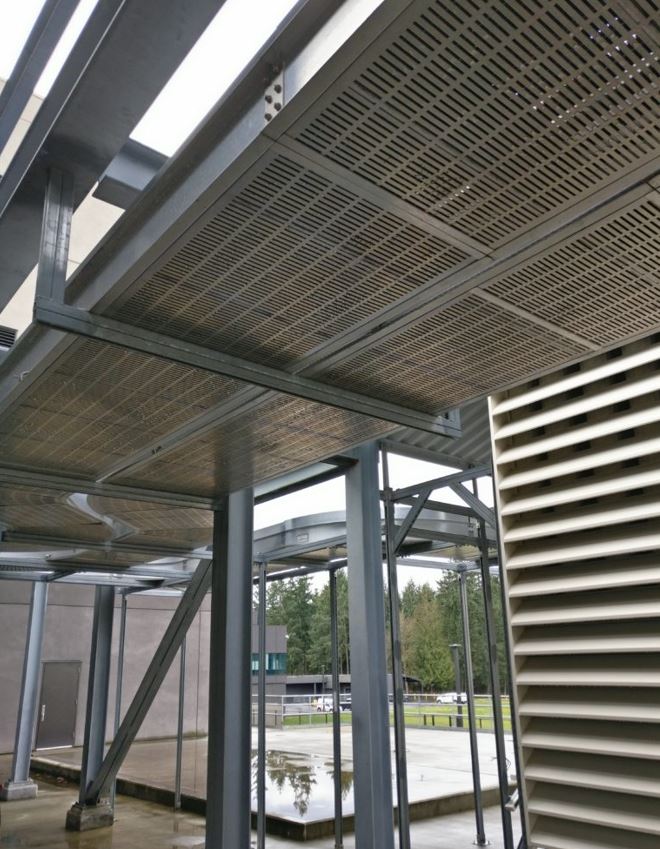
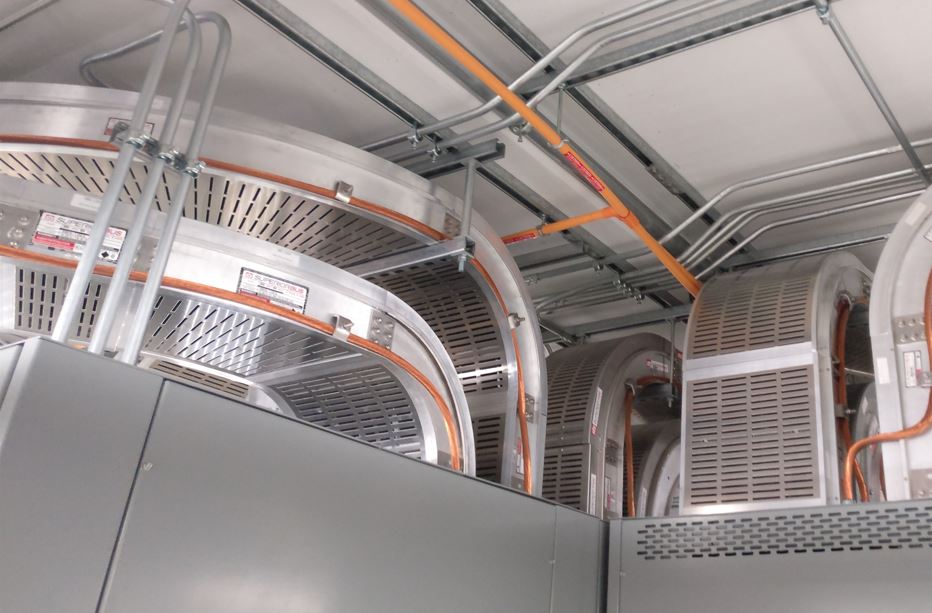
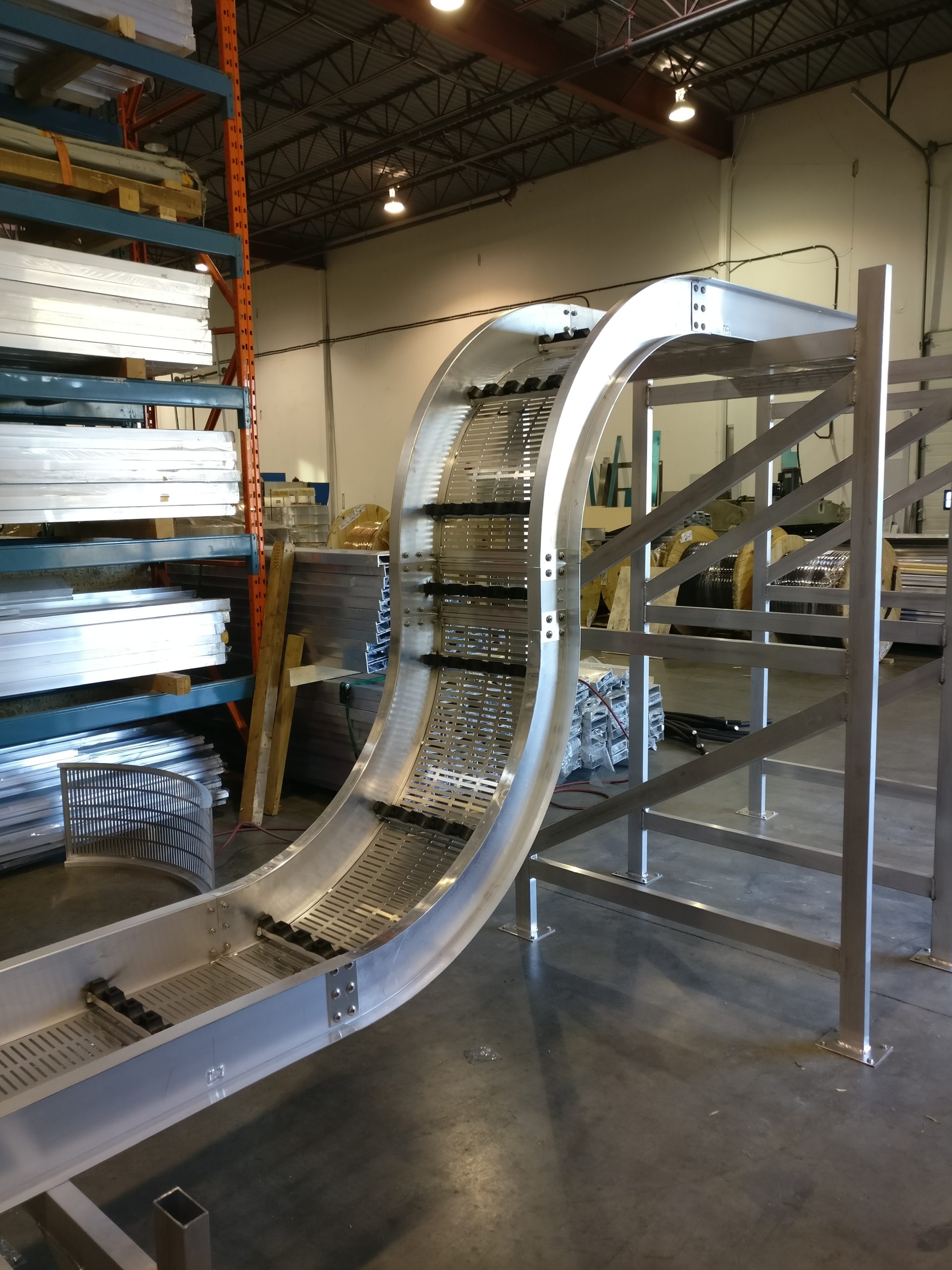
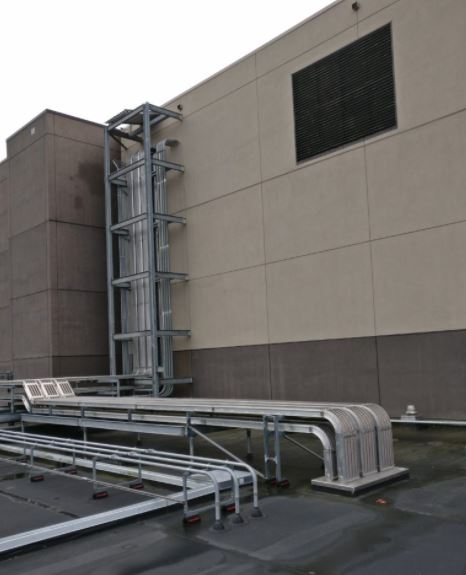
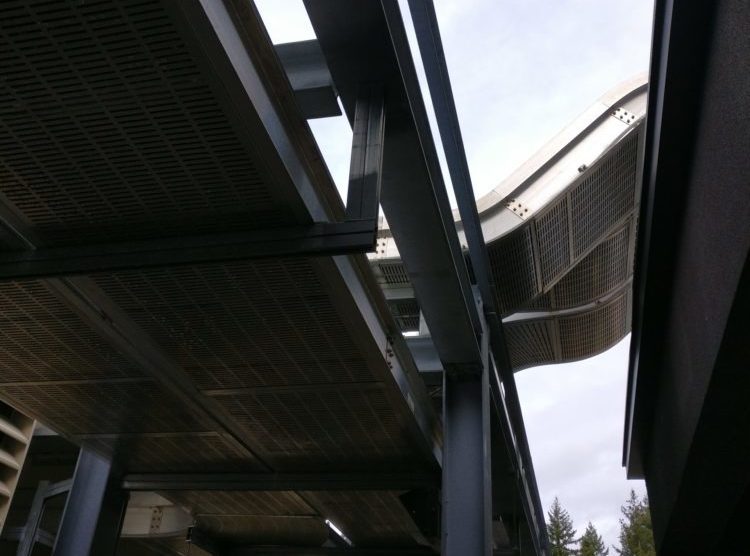
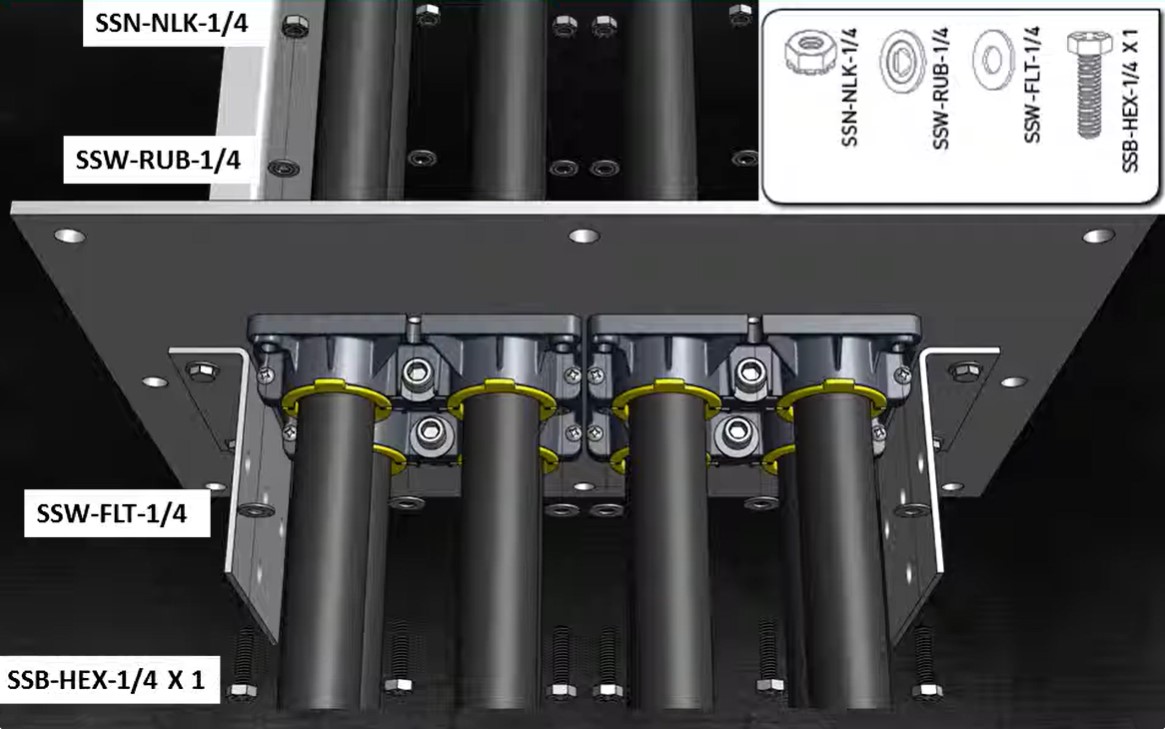
The superiorBus step-by-step installation guide For Your Cable Bus System SuperiorBus is an extremely versatile power feeder system It can be hung from the ceiling, wall mounted both indoors and out, and installed underground in a ventilated trench. We have the experience to help you specify the correct mounting, expansion, and support systems for your…
-
Harbor Energy Solutions and Superior Tray Systems at NECA Show 2023!
Organized by the National Electrical Contractors Association (NECA), the show opens doors for the entire industry, inviting everyone to explore, engage, and embrace novel solutions that promise to elevate their bottom lines. Your success, our success – let’s come together and shape the future of electrical construction. Harbor Energy Solutions: Your Premier Partner for Quality…
-
Which Is Better, Stranded or Solid Wire, And Why?
Wire harnesses and cable assemblies, among other electrical power distribution equipment use solid and stranded wires. While stranded wire is made up of multiple thinner wires twisted together to form a bundle, solid wires have a solid core. Each has unique advantages, and the best option for a given application depends on the particular needs…
-
Find Harbor Energy Solutions at the 2022 IEEE PES T&D Conference & Exposition
The IEEE PES T&D Conference & Exposition provides a once-in-a-lifetime chance for energy experts to reconnect and explore a variety of ideas driving industry development. A comprehensive technical program underpinned by IEEE’s prestigious standards, together with the most comprehensive presentation of breakthrough T&D solutions, will equips industry professionals to meet current and future challenges in…
-
Why Does Bus Topology Require Terminators?
A network topology refers to the geometric representation of how different nodes and devices are physically or logically interconnected to each other in a computer network. Physical topology is the configuration of computers, cables, and other peripherals while logical topology refers to the method used to pass information from one workstation to another. Learn More…
-
Cable Bus Vs Bus Duct
Cable bus and bus duct share certain similarities in system weight, power consumption, medium voltage drop, and enclosure size. However, they also have their differences that make electrical engineers favor one system over the other. What is Cable Bus? A cable bus is an electrical system that is made up of a ventilated metal casing…
-
Why Is Aluminum Used In A Busbar Instead Of Copper?
The evolution of the busbar system over the past few years has seen its increased usage and preference over hard-wired power distribution systems. Aluminum and copper are the two most common conductors used in electrical equipment. Of the two, copper is one of the oldest known metals used as a conductor of choice for most…